Benchmarking
„Benchmarking is the process of continuously comparing and measuring against other organisations anywhere in the world to gain information on philosophies, policies, practices, and measures which will help our organisation take action to improve its performance.”
/American Productivity and Quality Center/
Benchmarking is one of the three most popular management methods in the past few years. According to the survey of Bain & Company (see the table), in the year 2000 69% of the companies used it regularly (the two most popular methods were strategic planning and mission and vision statements).
The two most popular kind of benchmarking used by companies are: performance benchmarking and process benchmarking. Companies most often start benchmarking activities by measuring and comparing the performance of a selected area of company operations (diagnostic benchmarking). This is followed by the comparison of the total performance of the company with other companies (holistic benchmarking). Finally, the company starts to search for best practices applied by leading companies, maps the corresponding processes and adapts those practices to the local circumstances (process benchmarking).
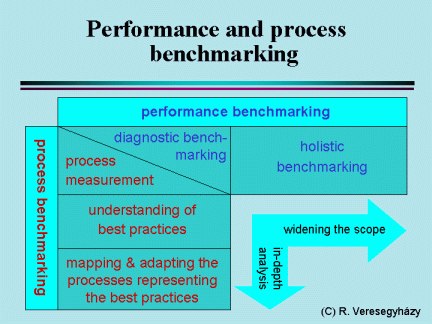
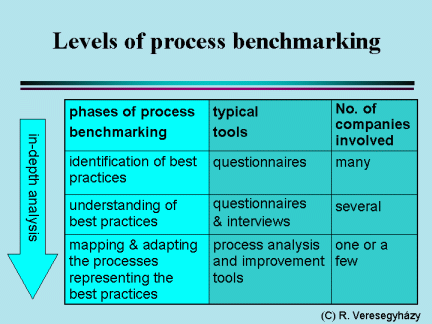
There is an overlapping of performance and process benchmarking at the diagnostic and process measurement phase. Holistic benchmarking is taking a step into the direction of widening the scope of the study, while process benchmarking is aiming rather an in-depth analysis of the processes representing the best practices. That requires the involvement of a varying number of companies and the use of different tools at the different phases.